Describing Your Data
Required Metadata
Title: The full title by which the dataset is known.
Examples:
- Acoustic recordings of North Atlantic right whale upcalls in the Gulf of St. Lawrence
- Impacts of the Husky oil spill on gut microbiota of native fish species to the North Saskatchewan River
Description: Provide a summary describing the purpose, nature, and scope of the dataset.
Example:
- “This file contains collated data of the AHR1 ligand binding domain subtypes, embryonic dioxin EC50 values, and 17 life history traits for 89 avian species. The traits included in this dataset are indicative of each species's developmental rate, fecundity, level of contaminant depuration into the egg, body size, longevity, migration strategy, range, habitat type, trophic level, and degree of sociality and sexual competition. Most birds in this dataset are North American species. These data are associated with the article, "Species traits predict the aryl hydrocarbon receptor 1 (AHR1) subtypes responsible for dioxin sensitivity in birds" by Bianchini and Morrissey (2020). The data were used to investigate the relationship between species traits, phylogeny, and AHR1 subtypes in birds.” (doi:10.20383/101.0257)
Keywords: List subjects, keywords, classification codes, and/or key phrases describing the dataset. You may include any terms, which may be taken from a controlled vocabulary (e.g. OCLC FAST). Geographic locations should be placed under Geographical Metadata.
Examples:
- Ornithology
- Sterna paradisaea
- Sea birds
- Migration
- rDNA
- Breeding
Field of Research: Choose one or more field(s) of research by using the Canadian Research and Development Classification field name(s) applicable to this dataset.
Fields of research are organized into Groups, which are subdivided into Classes. To find the field(s) of research applicable to your dataset, use the dropdown menus for Group, Class, and Field. You may also browse the classification in English or French using Statistics Canada documentation:
- Research and Development Classification (CRDC) 2020 Version 1.0 - Field of Research (FOR)
- Classification Canadienne de la Recherche et Développement (CCRD) 2020 version 1.0 - Domaine de recherche (DDR)
Select as many fields as appropriate to describe the dataset. If your field of research is not listed, choose one of the fields containing “not elsewhere classified”.
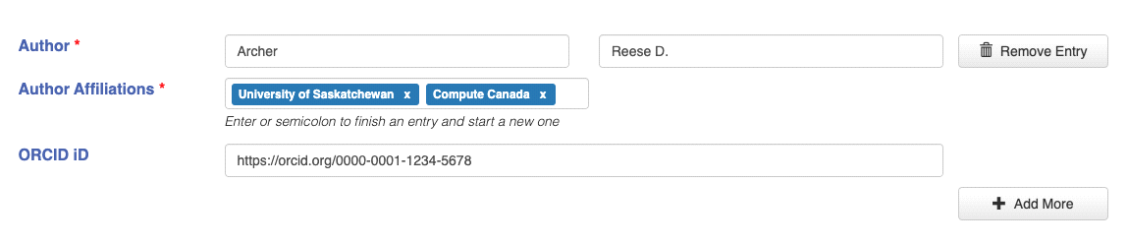
Author: Enter the name, affiliation(s), and ORCID iD for each author or researcher who produced the dataset. You may include multiple authors.
- Author: Enter the Last Name and First Name.
- Author Affiliations: List the organizational or institutional affiliation(s) of the author. You must include at least one affiliation for each author.
- Enter additional affiliations by using the Enter key or a semicolon.
- Where possible, choose author affiliations by selecting from the auto-complete options. If your affiliation is not listed, you may enter a custom affiliation.
- ORCID iD: (optional) An ORCID iD is a unique, persistent identifier for a person. If available, enter the author’s 16-digit ORCID iD. You can find out more about ORCID here: https://support.orcid.org/hc/en-usr
Examples:
- Author with single affiliation and ORCID iD:
- Author: Archer, Rese D.
- Author Affiliations: University of Saskatchewan
- ORCID iD: 0000-0001-1234-5678
- Author with multiple affiliations and ORCID iD:
- Author: Archer, Rese D.
- Author Affiliations: University of Saskatchewan; Compute Canada
- ORCID iD: 0000-0001-1234-5678
Contact Information: Supply the name and email address of the person to contact about using this dataset. The email address will not be shown to the public; instead, a form will be shown for people to fill out if they wish to contact someone about using the dataset.
- Contact Name: Enter the Last Name and First Name of the person to contact with questions about the dataset.
- Contact Email: Provide the email address of the person to contact with questions about the dataset.
Example:
- Contact Name: Archer, Rese D.
- Contact Email: rese.archer@frdr-dfdr.ca
Rights: Users submitting a dataset will have a choice of licensing terms regarding the use of their data by others. The license terms will be displayed on the landing page of FRDR datasets.
Submitters will be required to choose a license. The following are the default options (recommended):
- Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication (CC0 1.0)
- Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
The following licenses may also be selected by clicking the “More” button:
- Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0)
- Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 (CC BY-NC 4.0)
- Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
- Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Note that a Curator may ask why you are unable to make use of the default licenses. For other licensing terms not found here, or for customized data use licenses, contact support@frdr-dfdr.ca.
Recommended Metadata
Time Period Covered: The date or date range to which the data refers. This field reflects the time period covered by the data, not the dates of coding, analysis period, or the dates the data was collected. Enter start and/or end dates in YYYY-MM-DD, YYYY-MM, or YYYY format.
Examples:
- 2010-02-12/2010-02-28
- The data is about the time period from February 12, 2010 to February 28, 2010.
- 1984-01-01/1984-12-31
- The data is about the year 1984.
- 2020-03/2020-12
- The data is about the time period from March 2020 through December 2020.
- 1990/1999
- The data is about the time period from 1990-1999.
Collection Period: The date or date range in which the data was collected. Enter Start and/or End dates in YYYY-MM-DD, YYYY-MM, or YYYY format.
Examples:
- 2010-04-01/2010-06-30
- Data collection began on April 1, 2010 and ended on June 30, 2010.
- 1985/1986
- Data collection began in 1985 and ended in 1986.
- 2021-01/2021-03
- Data collection began in January 2021 and ended in March 2021.
- 2000/2009
- Data collection began in 2000 and ended in 2009.
Funding Information: Enter the funder name, award number, and/or award title for this dataset. You may include multiple funders. A funder name is required for an award number or award title to be entered.
- Funder: Enter the name of the funding provider.
- Enter additional funders by using the Enter key or a semicolon.
- Where possible, choose funders by selecting from the auto-complete options. If your funder is not listed, you may enter a custom funder.
- Award Number: (optional) The number or code assigned by the funder to a sponsored award or grant.
- Award Title: (optional) The title or name of the award or grant.
Example:
- Funder: Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)
- Award Number: 123456
- Award Title: Migration Ranges of Arctic Terns
Contributor: List additional people and/or institutions responsible for contributing to the dataset. When entering a person’s name, enter in the format Last Name, First Name. For each contributor, select the type of contributor from the dropdown menu.
Example:
- Data Collector: Archer, Rese
- Research Group: Information Visualization Lab
Refer to the following definitions for each contributor type (taken from the DataCite Metadata Schema 4.3):
Contributor types
- Data Collector: Person/institution responsible for finding, gathering/collecting data under the guidelines of the author(s) or Principal Investigator (PI).
- Data Manager: Person (or organisation with a staff of data managers, such as a data centre) responsible for maintaining the finished resource.
- Project Manager: Person officially designated as manager of a project. Project may consist of one or many project teams and sub-teams.
- Research Group: Typically refers to a group of individuals with a lab, department, or division; the group has a particular, defined focus of activity.
- Sponsor: Person or organisation that issued a contract or under the auspices of which a work has been written, printed, published, developed, etc.
- Note: For persons or institutions providing funding, use the Funder field instead of the Sponsor contributor type.
- Supervisor: Designated administrator over one or more groups/teams working to produce a resource or over one or more steps of a development process.
- Other: Any person or institution making a significant contribution to the development and/or maintenance of the resource, but whose contribution does not “fit” one of the other contributor types.
Related Identifiers: Provide links to resources related to the dataset. If a DOI (digital object identifier) is available, provide the DOI (e.g. https://doi.org/10.1000/182); otherwise, a URL is sufficient. For each related resource, select the relationship between the dataset and the related resource from the dropdown menu.
Example:
- this dataset is cited by: https://doi.org/10.1000/182
Relation types:
- this dataset is cited by: The dataset is cited by the related resource. Typically, this means that the related resource includes the dataset in a formal citation. Since publications have varying practices for data citation, FRDR’s definition includes both formal citations and other links to the dataset (for example, in a “data availability” section or in the body of the paper). In general, this option should be selected for publications that analyze the dataset.
- this dataset cites: The dataset cites the related resource. This includes related resources that are listed in the README file (for example, a paper describing a protocol). This relation type is often used for a related resource which describes a methodology in general terms, published before the dataset being deposited was collected. For a related paper that analyzes the dataset and describes the methodology, use “this dataset is cited by”.
- this dataset is a supplement to: The dataset supplements the related resource. This includes publications that analyze the dataset, but do not cite the dataset (for example, if the paper was published before the dataset was made available in FRDR).
- this dataset is supplemented by: The dataset is supplemented by the related resource (or, the related resource is “supplementary material” to the dataset). For example, software used to analyze the data may be considered supplementary material.
- this dataset is part/subset of: The dataset is a part, or subset, of the related resource. For example, the dataset is part of a larger series.
- this dataset has part/subset: The dataset has a part, or subset, represented by the related resource (or, the related resource is a part or subset of the dataset). For example, the related resource is a portion of the dataset.
- this dataset is derived from: The dataset is derived from the related resource. For example, the dataset could be aggregate data summarizing survey data (the related resource), or produced by analyzing the related resource.
- this dataset is the source of: The dataset is the source of the related resource (or, the related resource is derived from the dataset). For example, the related resource was produced by analyzing the dataset.
- this dataset is compiled / created by: The dataset is compiled or created by the related resource. For example, the related resource is a simulation program that created the dataset.
- this dataset compiles / creates: The related resource is compiled or created by the dataset (or, the dataset compiles or creates the related resource). For example, the dataset is a model that was used to generate the related resource.
- this dataset is continued by: The dataset is continued by the related resource. For example, the related resource is the next dataset in a chronological series of datasets, such as annual survey data.
- this dataset continues: The dataset is a continuation of the related resource. For example, the related resource is the previous dataset in a chronological series of datasets, such as annual survey data.
Notes: Any additional important information about the dataset. Notes can be used for information that is not covered by the other metadata fields, including information that is included in the README. For example:
- Information about file structure, i.e. a high-level overview of the relationship between the folders/files in the dataset
- Information about an instrument used to collect the data
- Information about software that can be used to interpret the data
- Information about a metadata schema or standard that was used to structure the data
- Additional information about related items:
- Further explanation of a relationship between the dataset and an external item linked in the Related Identifier field, such as a software package or related dataset
- References to related items that do not have a URL or DOI, and therefore cannot be included in the “Related Identifier” field
- Additional acknowledgements that are not covered by the Contributor or Funding Information fields
- Additional notes for researchers who are re-using the dataset (for example, a request to contact the authors to discuss collaboration opportunities).
Geographical Metadata
Geographic Coverage: The geographic coverage of the dataset — i.e., the location(s) that the dataset is about. For each place name, enter as many fields as applicable to describe the location. Use GeoNames for correct spelling of place names and avoid abbreviations.
- Place Name: General information on the geographic coverage of the data. Use for geographical names that are not a country, province/territory/state, or city; e.g. regions, water bodies, astronomy names, and alternate names.
- Country: The country or nation that the dataset is about. If the dataset covers multiple countries, list all of them separately.
- Province / Territory / State: The province, territory, or state that the dataset is about.
- City: The name of the city that the dataset is about.
Example:
- Place Name: Stanley Park
- Country: Canada
- Province / Territory / State: British Columbia
- City: Vancouver
Geographic Point: Point where the data was gathered or about which the data is focused. Provide latitude and longitude.
- Latitude: Latitude: Latitude: Decimal degrees between -90 and +90.
- Longitude: Longitude: Longitude: Decimal degrees between -180 and +180.
Example:
- Latitude: 49.2827
- Longitude: -123.1207
Geographic Bounding Box: Spatial region where the data was gathered or about which the data is focused. Provide a bounding box with decimal degree coordinates.
- West Longitude: Westbound coordinate of the bounding box. Decimal degrees between -180 and +180.
- East Longitude: Eastbound coordinate of the bounding box. Decimal degrees between -180 and +180.
- North Latitude: Northbound coordinate of the bounding box. Decimal degrees between -90 and +90.
- South Latitude: Southbound coordinate of the bounding box. Decimal degrees between -90 and +90.
Example:
- West Longitude: -123.121
- East Longitude: -123.005
- North Latitude: 49.297
- South Latitude: 49.203